If you want to understand dns working & what are the components of dns then keep on reading as in this article i’ll be explaining to you in detail about what it is & components of dns & why is dns required. To understand working of dns let’s take an example of telephone directories.
Before the era of mobile phones, all we had was just wired Telephone instruments also referred to as Landlines to make calls. Everyone had a thick, heavy phone directory or book also known as white/yellow pages at their home which was filled with numbers of all telephone subscribers in a geographical region. Its purpose was to allow anyone to easily find telephone number of a person/organization identified by name or address.
After the arrival of mobile phones there was no longer need of a physical book to be maintained as mobiles allowed us to store information digitally inside them.
Whenever you call your mom, first you search for her name in contact directory of your mobile phone & once it is found you simply hit the dial button. Your mobile phone then automatically dials the right number at which you can reach out to her because your phone maintains a directory of its own & knows which contact name corresponds to which number.
You browse numerous websites over the internet and type URLs like www.facebook.com, www.youtube.com, google.com etc. but have you ever wondered how exactly your browser differentiates between URLs & determines the right server/website to access? If not then I will let you know in the course of this blog.
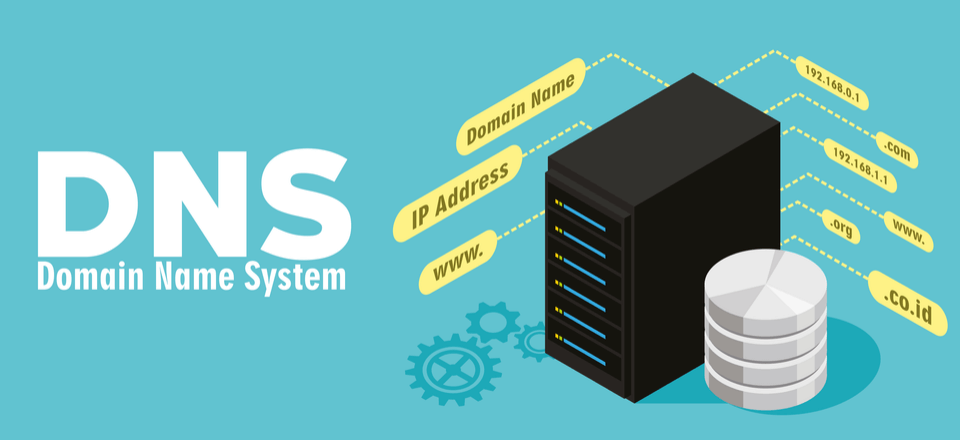
Any device connected to a network or Internet is uniquely identified by its IP Address, a numeric label which serves two main purposes: network interface identification & Location addressing. IP addresses are written & displayed in human readable form such as 172.16.254.1 or 192.168.1.15, you can read more about it (here) Wikipedia link .
We use domain names instead of IP addresses to access websites as names are more readily memorized than few seemingly random numerical digits.
A Domain Name System is a system, decentralized & hierarchical in nature that maps such readily memorized domain names to numerical IP addresses that a computer uses to locate a website.
DNS WORKING? Or The Components of DNS
1) The Query
When you type say www.xyz.com in your browser, you generate a query that is sent over the internet to find website for www.xyz.com . A query is a request to match domain name to corresponding IP address.
The first type of server that your query interacts with is called recursive resolver which is operated by your wireless carrier, Internet Service Provider or maybe a third party provider.
The recursive server knows which other DNS Servers it needs to answer your original query “What is the IP address of xyz.com?”
2) Root Servers
The type of DNS Server with which recursive resolver talks to first is called Root Server. The Root Servers are present all over the world and each root server knows DNS information about Top Level Domains. To begin answering your query the resolver asks for DNS Information from a root server about .COM .
There are thousands of servers strategically located to support the root according to where the most internet activity occurs. The DNS ensures that your query isn’t send to a server that is too far.
3) The TLD or Top Level Domain Name Server
Each top level domain (TLD) DNS name server stores the address information for the second level domains (xyz.com) within the top level domain (.com). When your query reaches the Top Level Domain (TLD) server, the TLD server answers with the IP address of the domain’s name server, which will provide next piece of the puzzle.
4) Domain’s Name Sever
Next, the recursive resolver sends the query to the domain’s name server. This DNS knows the IP address for the full domain, xyz.com, and that answer is returned to the recursive resolver.
As now Internet supports more and more users, content & applications, the original IP address standard, IPv4 will transition to IPv6.
At the end i hope that now you’d have a better understanding about dns, components of dns & how dns works